[146] Delamination diagnosis system using nonlinear transformation-based augmentation approach for CNN transfer learning
D. Y. Kim, Y. J. Woo, S. G. Sim, and G. H. Yoon. Journal of Vibration Engineering & Technologies 12.3 (2024): 3213-3230.
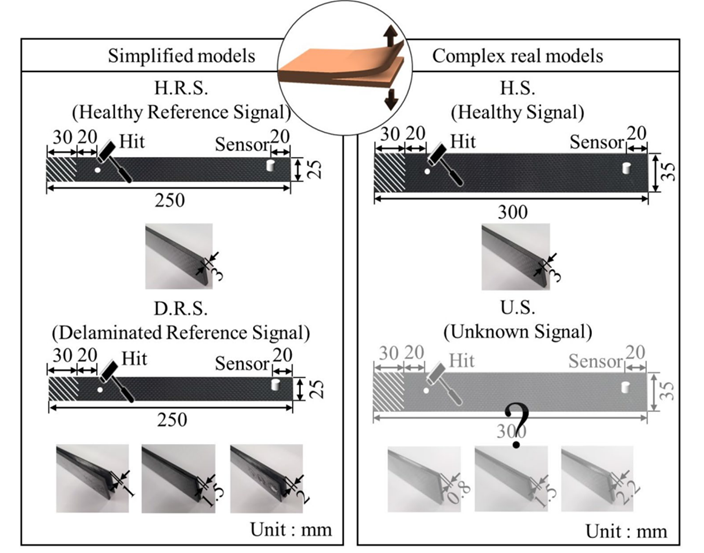
Purpose This study presents a nonlinear transformation-based data augmentation approach to diagnose delaminations such as interlaminar, through-hole and buckle, in relatively complex composites. The approach uses tailored vibration signals of relatively simplifed composites and employs a convolutional neural network (CNN). Methods The present study involves modeling several composite structures with and without interlaminar, through-hole and buckle delaminations using fnite-element method (FEM)-based simulation. A vibration experiment is also conducted for the case of interlaminar delamination. In our method, it is assumed that all vibration signals of simplifed composites and healthy condition of complex real composites are obtained that paves the way to investigate the delamination conditions of real composites. Then, the present approach adopts the nonlinear transformation method mapping the signals of complex healthy composites and simplifed healthy composites. The diference between the transformed signals of complex real composites and the reference signals of simplifed composites is utilized for the virtual spectrogram computed by the short-time Fourier Transform (STFT). These virtual spectrograms fed into a CNN-based diagnosis system to diagnose the types and locations of delaminations. Results For interlaminar cases, the simulation and experimental vibration signals are diagnosed with 100 and 92.5%, respectively. Through-hole and buckle cases are both diagnosed with an accuracy of 100%. Using nonlinear transformation to classify vibration signals prior to diagnosis has been shown to be highly advantageous for delamination diagnosis. Conclusion The results allow the diagnosis of three cases of complex composites with simplifed composites using the delamination diagnosis system.