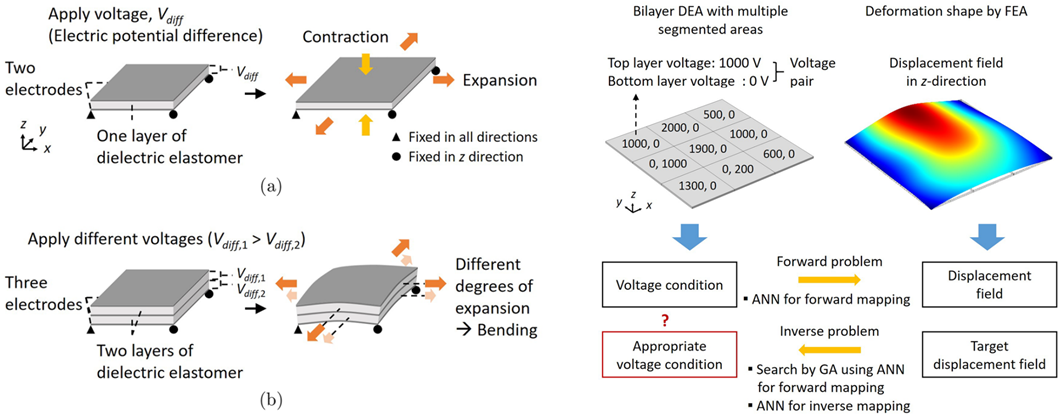
[129] Determination of voltage condition for target displacement field of dielectric elastomer actuator using artificial neural network
K. H. Kim and G. H. Yoon. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization 66, no. 6 (2023): 1-27.
In this study, we explore the feasibility of the artificial neural network (ANN) model in the inverse problem that determines the voltage condition for implementing a desired deformation of the dielectric elastomer actuator (DEA). Our main focus is on the effectiveness of two basic approaches based on supervised learning in the inverse problem of DEA. In the first approach, the forward problem of computing the vertical displacement field of DEA using finite element analysis (FEA) is replaced by ANN. Then, a genetic algorithm (GA) is employed to find the optimal voltage condition using the ANN for forward mapping. In the second approach, the inverse problem is directly solved using the ANN for inverse mapping. Although a supervised learning-based approach requires a data generation process and is data-dependent, it can be considered as an easy-to-use tool for a variety of engineering problems and can be the basis for applying advanced optimization techniques. In the present work, a bilayer DEA with segmented regions for different voltage applications is considered to implement various curved deformations. In terms of conducting an initial study, voltage conditions are simply expressed as a 3 × 3 matrix and displacement fields as a 12 × 12 matrix. To compare the two approaches, an example of finding the voltage condition that similarly imitates an arbitrary target displacement field is provided. The first approach is better in terms of accuracy when the target displacement field is abstract and far from the characteristics of the training data of ANN. Conversely, the second approach is better in terms of real-time prediction when the target displacement field is more realistically generable.