[128] Vibration and sound pressure reduction over a wide frequency range with an optimal dynamic vibration absorber
S. J. Han, D. H. Kim, and G. H. Yoon. Journal of Low Frequency Noise, Vibration and Active Control 42, no. 2 (2023): 935-951.
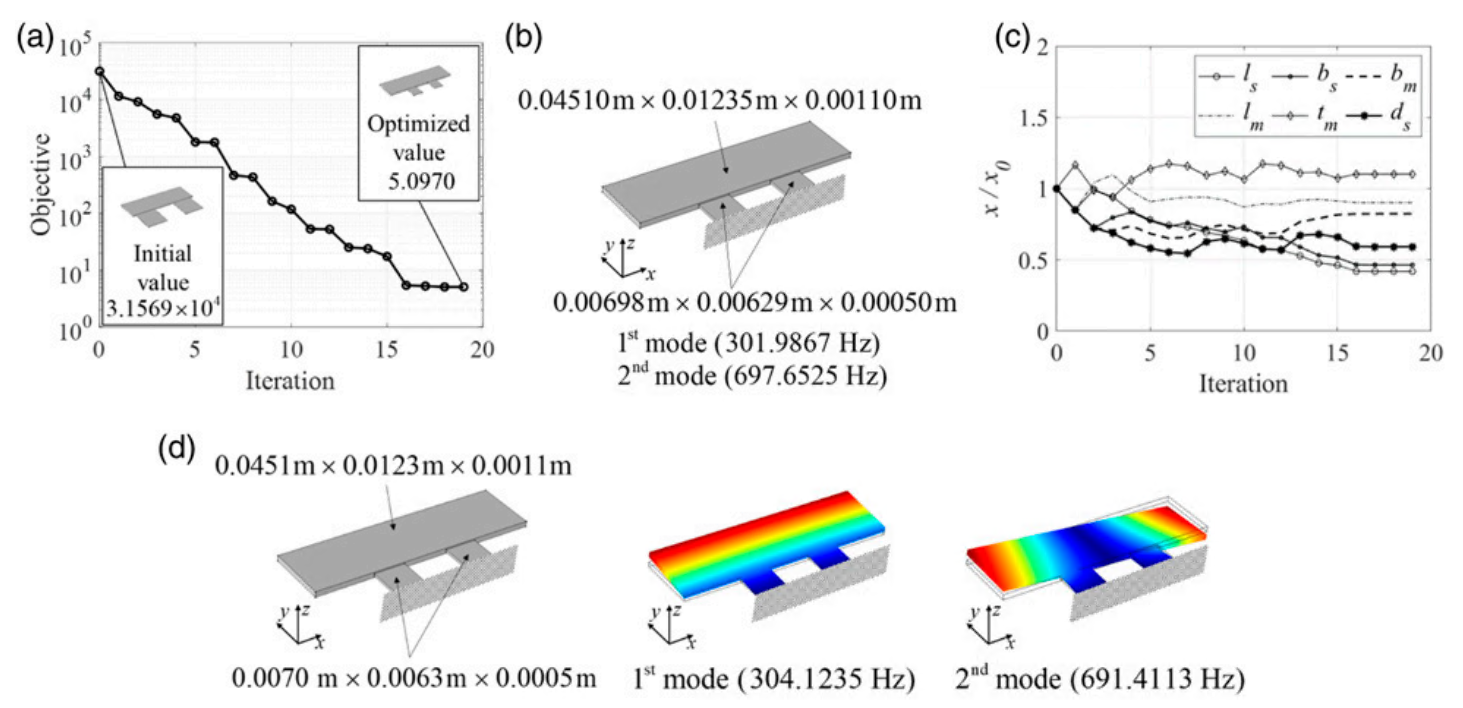
In this study, an optimized dynamic vibration absorber (DVA) was applied to improve the sound absorption performance and simultaneously attenuate vibrations and structure-borne noise at multiple frequencies. As the size parameters and eigenfrequencies of a DVA demonstrate a nonlinear relationship, tuning the eigenfrequencies by heuristically modifying the geometric parameters of the DVA is difficult. To avoid this intricate process, geometric parameters were optimized using a gradient method solver to tune the eigenvalues of the DVA to the target frequencies. Post-processing was performed for the sake of manufacturing. To confirm the validity of the performance of the sound absorption and vibration/noise attenuation, impedance tube experiments and impact experiments were conducted using the manufactured DVA. The impedance tube experiment verified that the values of the sound absorption coefficient increased with the application of the DVA. From the impact experiments, it was verified that the values of the frequency response function and sound pressure level decreased with the application of the DVA. The present study validates the notion that optimized DVAs improve the sound absorption performance of structures and simultaneously reduce vibrations and sound pressures at multiple desired frequencies.