[68] Optimal design of the PMSM retaining plate with 3-D barrier structure and eddy-current loss-reduction effect
H. W. Jun, J. W. Lee, G. H. Yoon, and J. Lee. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics 65, no. 2 (2017): 1808-1818.
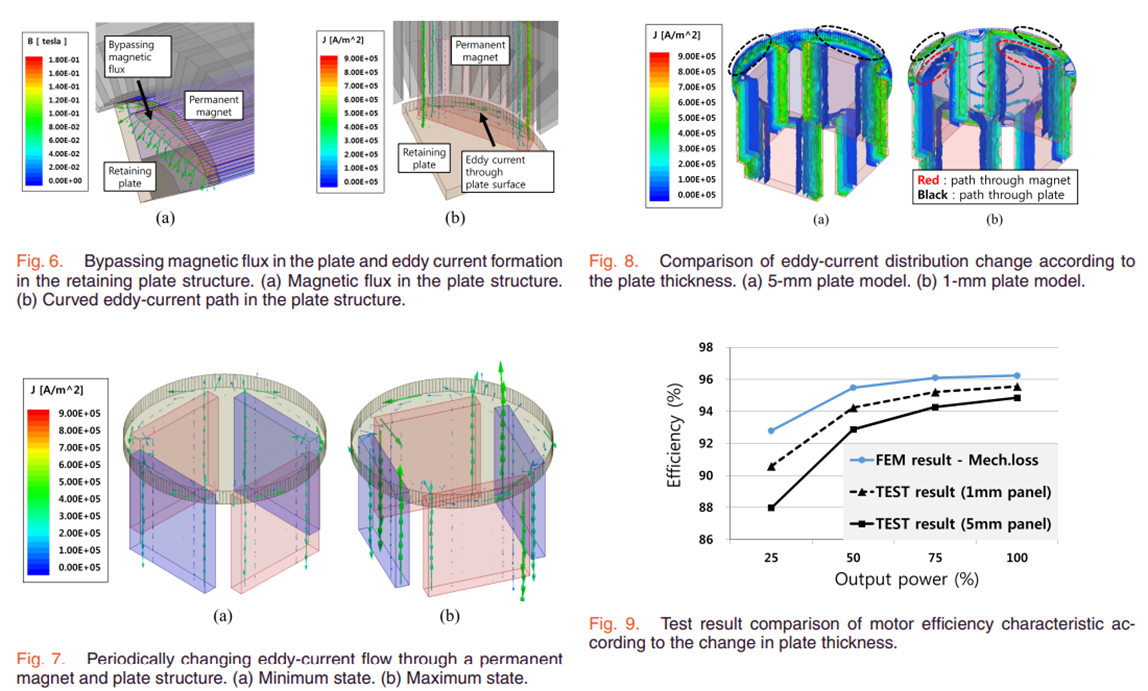
From the constant-speed variable-output motor driving test result of an interior permanent-magnet synchronous motor for a pump drive, we observed that there was an additional loss factor, which was not previously considered. Furthermore, a 3-D finite-element method analysis was performed to investigate the cause of the additional electromagnetic loss. Accordingly, it was confirmed that there was an additional eddy-current loss in the rotor retaining plate structure for the rotor assembly. Using the shape of the eddy-current path in the plate, it was determined that the eddy current was formed inside the plate itself by the bypassing magnetic flux from the permanent magnet and the slot harmonics. It was confirmed that the eddy-current path can be changed according to the structure of the plate, and the optimal retaining plate design that satisfies the design constraints was derived via the topology optimization method. Finally, the retaining plate design with the 3-D barrier structure was derived by arranging the void shape considering the total eddy-current path. Using the actual model test results, it was verified that the new retaining plate design was effective for loss reduction compared to the conventional structure.